Building through virtual walls
The use of intelligent helmets could improve the safety and productivity of the construction crew

Let's imagine for a moment that you join a construction team that is working on a new project: a large office building. While you're waiting for the installation of the HVAC systems, you look at the ceiling, wondering what's behind of it. To do it, you pull up your tablet with a BIM model, which is instantly projected in front of you. On it, you can see the heating ducts, water pipes, and electrical boxes along the corridors, while you walk across through the construction. Removing the different layers of the model we will find the building's steel structure, the insulation and what were the chosen materials. It seems like science fiction but soon will be a reality and not very far from your town.
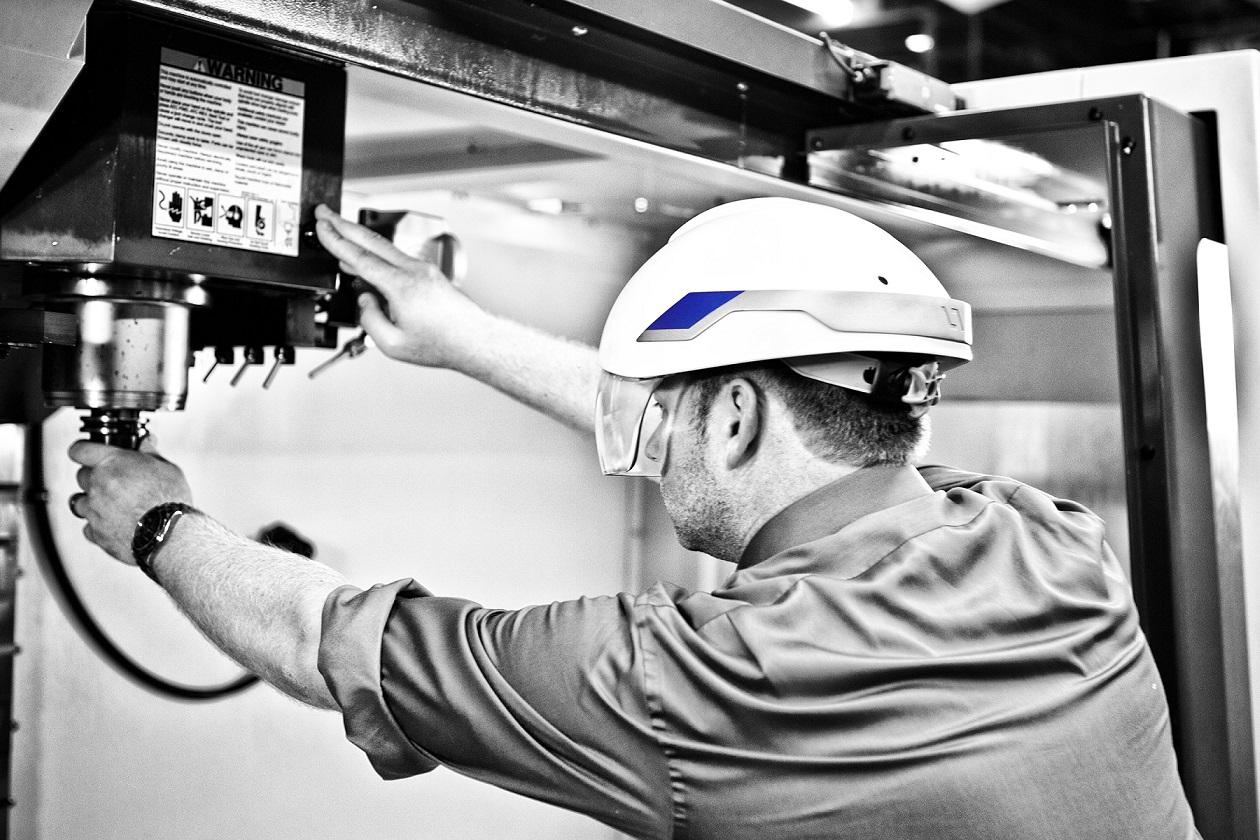
Through the DAQRI Smart Helmet, a portable augmented-reality system being used in the industrial fabrication companies, builders, engineers, and designers can bring their BIM models to the construction site, wearing it on their heads, and be able to experience a full-scale 3D environment. Providing access to the construction teams to this level of building information will allow them to see better the spatial relations, besides of detect MEP clashes earlier and being able to work with few errors and better-documented decisions. With this new technology, the worker can make decisions in the field itself, instead of waiting to the end of the shift or the construction phase. The power now belongs to the end construction worker.

The failure of previous tools such as Google Glasses, hasn't stopped the industry to keep trying to improve in the VR field, is because of that DAQRI is focused only on industrial applications. That provide fewer complications while working with them, especially with the privacy concerns. The helmet works with three different types of cameras that allow users to target a specific point in space and track the geometry around them. That is because of the 166-degree wide angle lens that provides the user position with an accuracy of a few centimeters. Besides of that, the helmet is equipped with a depth-sensing camera that reads the main objects around the subject, providing information such as doors, windows, furniture... Knowing that is much easier to make changes in the model itself and creates a map of all the space of the building, based on the temperature readings.
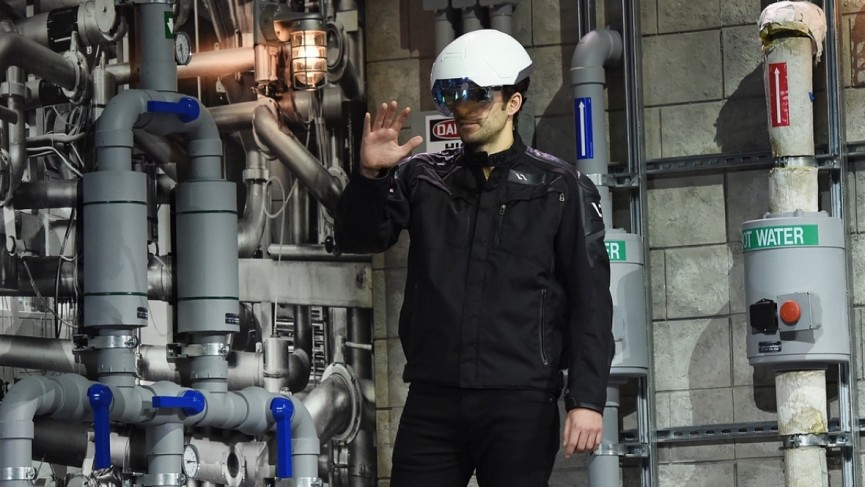
One of the main motivations of the DAQRI helmet software was promoted to avoid the risks at the construction works. At the beginning, hand signals were used to be picked up by the camera and memorized. This experiment didn't work because the technology is still not mature enough to provide an accurate reliability. Besides, the construction site is not the perfect place to be moving your hands on the air. If we don't pay attention to what we are doing is easy to get hurt with sparks spinning blades or tons of metal, flying through the air.
To solve those worries, the DAQRI has been designed to be used without the hands, and based on a system called "gaze and dwell system", operated only with their heads. Almost like a mouse over an element, once it is selected, it gets highlighted.The helmets are equipped with Autodesk BIM 360, but the DAQRI company encourages the users to create their own software because of the versatility of the product.
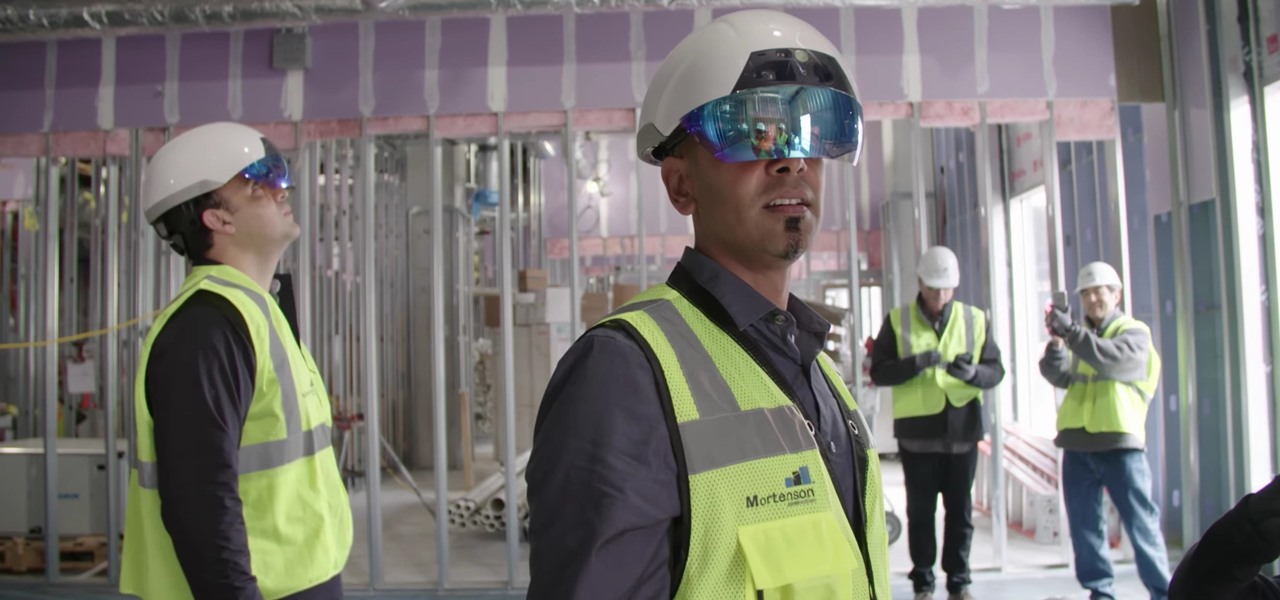

The use of DAQRI provides multiple benefits, especially in the construction phase but it is worth it to try it as well in the day-to-day of an engineer. That could allow the architect to show the rest of the team and the constructor the model before building it, in order to find possible mistakes and problems. Fixing them on the design phase will save a lot of money and time. This kind of system could provide construction crews a list of instructions for the punch-list inspections or even once the building has been finished.
Augmented reality has far-reaching impacts in how the society is going to interact with information in the context of the environment. For the industry is very important to keep working on that in order to face a lot of problems such as safety of the crew, making them aware of the importance of it. On the other hand, customers can improve the facility management of the different facilities.
Initiatives such as DAQRI are working in the way buildings are made, but there's still a lot to do regarding the integration between the real building and its virtual representation. The next challenge will be to create a device capable of detecting hidden elements to the sight and then, be able to represent them dynamically to the users, even if they're included or not in the model. That would to the augmented reality to the top of the X-ray vision, and the construction industry to a whole new technological level.