Technical Area | Articles
The place to solve all your BIM doubts
Integration of BIM with Facilities Management
BIM Implementation Strategies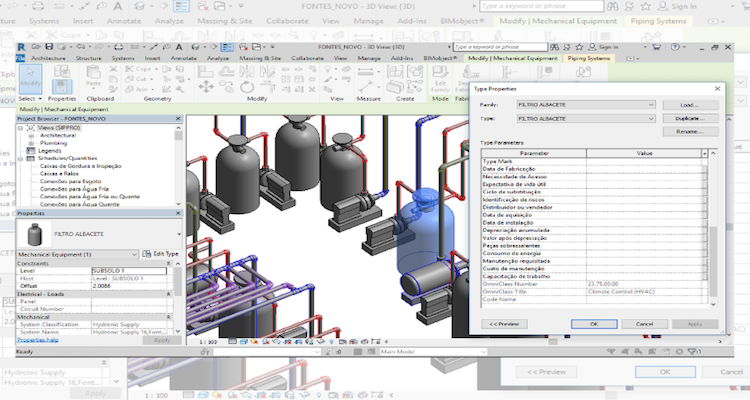
Building Information Modelling (BIM)
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a working methodology that directly influences the main pillars of an organisation: people, policies, processes, technology and data. What these pillars have in common is the importance of the correct use of information throughout the building life cycle process, from planning to demolition. Thus, BIM can be seen as a large database in the form of a 3D geometric model that helps to achieve higher quality projects in less time and at lower cost.
The main advantages of BIM include the following: (i) Collaboration between multiple disciplines; (ii) Facilitated verification of project intentions; (iii) Rapid reaction to construction problems; and (iv) Support to building management.
BIM in the building life cycle
In general, buildings have a life cycle segmented into the following phases: Planning, Design, Construction, Installation, Occupancy, Operation, Maintenance, Revitalisation, Dismantling and Demolition. The implementation of BIM at the beginning of the cycle contributes to the project process and collaboration, which makes BIM a fundamental component for information continuity. Figure 01 presents the information path associated with the life cycle phases in order to mitigate the loss of information during phase transitions.
The operation phase, being the longest phase, is the most costly compared to the other phases. The advantage of using a BIM model in this phase is the easy access to specific information quickly and efficiently for use in the management and operation of the building.
Facilities Management
Facilities Management (FM) is a multi-disciplinary activity that ensures the functionality of a building, integrating people, environment, processes and technology. It aims to ensure that the working environment does not hinder the productivity of the core business or the workers. The main benefits of FM include (i) Integration of the different service processes throughout the building; (ii) Linkage within the building at strategic, tactical and operational levels; and (iii) Consistent communication between the manager and the users.
BIM with Facilities Management
There are several ways in which BIM can be used to improve Facilities Management processes: (i) ease of access to real-time data; (ii) maintenance verification; (iii) asset management (Figure 02); (iv) space management; and (v) energy monitoring and control (Figure 03).
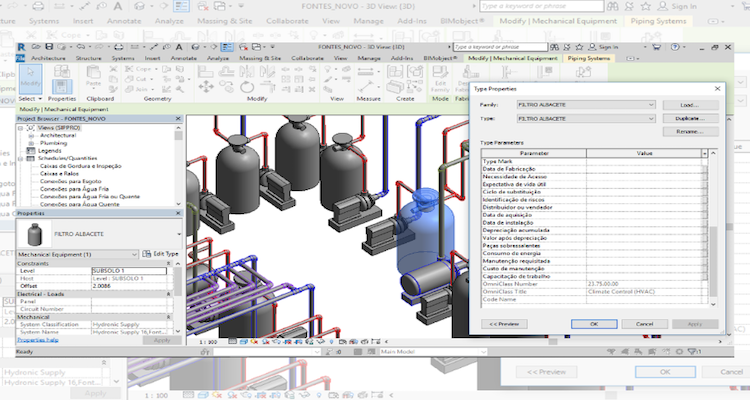
Figure 02 - Use of the model for asset management. Source: Mota, 2017
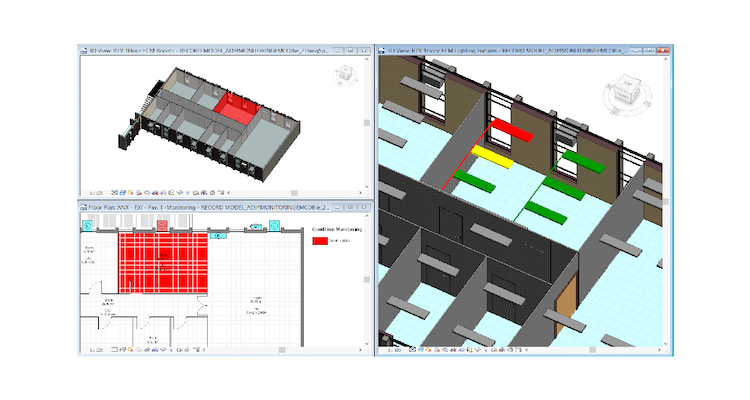
Figure 03 - Use of the model for energy control and monitoring. Source: Machado, 2018
However, it is important to note that the information necessary for the management of these processes must be inserted into the BIM model. It must be clear what information is requested, whose responsibility it is to insert the information and what is the appropriate timing of insertion of this information.
Level of information required
Once the importance of the correct insertion of information is understood, it is possible to make a relationship between the main stages of the building life cycle with the level of information associated in the BIM model for use in the FM.
In the project phase, for example, the need for graphical information is high and the amount of information allocated is low. This phenomenon is justified by the need to visualise shapes, spaces and objects during project conception. As the process progresses, additional information needed on materials, environments and equipment is introduced to assist in the execution of the works.
For the construction phase, more information and details are needed, such as cost estimation, procurement, coordination, construction processes and installations. Finally, after construction, installation and testing of systems and equipment, the latest information can be entered into the BIM model and made available to the management system.
Final considerations
This article aimed to present two management methodologies, BIM and Facilities Management, which can be associated for the greater benefit of the agents involved. It is possible to perceive that the synergy of BIM and Facility Management is directly associated to the quality of the information shared throughout the life cycle. This is reflected in a high added value of the building, reduced operating costs, project quality and easy access to information.
References
MOTA, Paula Pontes. "BIM model for asset management, 2017". 1 online resource (123 p.). Tesis (maestría) - Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Faculdade de Engenharia Civil, Arquitetura e Urbanismo, Campinas, SP. Disponible en: <http://www.repositorio.unicamp.br/handle/REPOSIP/331068>. Accessed on: 29 mar, 2021.
MACHADO, Fernanda Almeida. "BIM and Internet of Things for monitoring building energy consumption, 2018". 1 online resource (208 p.). Tesis (maestría) - Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Faculdade de Engenharia Civil, Arquitetura e Urbanismo, Campinas, SP. Disponible en: http://www.repositorio.unicamp.br/handle/REPOSIP/334629. Accessed on: 29 mar, 2021.
Author: Paula Mota, Engineer and Urban Architect. Master in Architecture, Technology and City (Universidade Estadual de Campinas - UNICAMP). Professor of the International Master in BIM Management - ZIGURAT E-learning. Director of BIM at SIPPRO. Consultant in BIM Maturity Assessment in global companies. Researcher of BIMe Initiative and Project Manager of the project MUT 4040 - Model Use Template.
Source: https://bit.ly/3B6zjR3