The Hungarian State Opera
Project
Published by:
Datasheet
Description
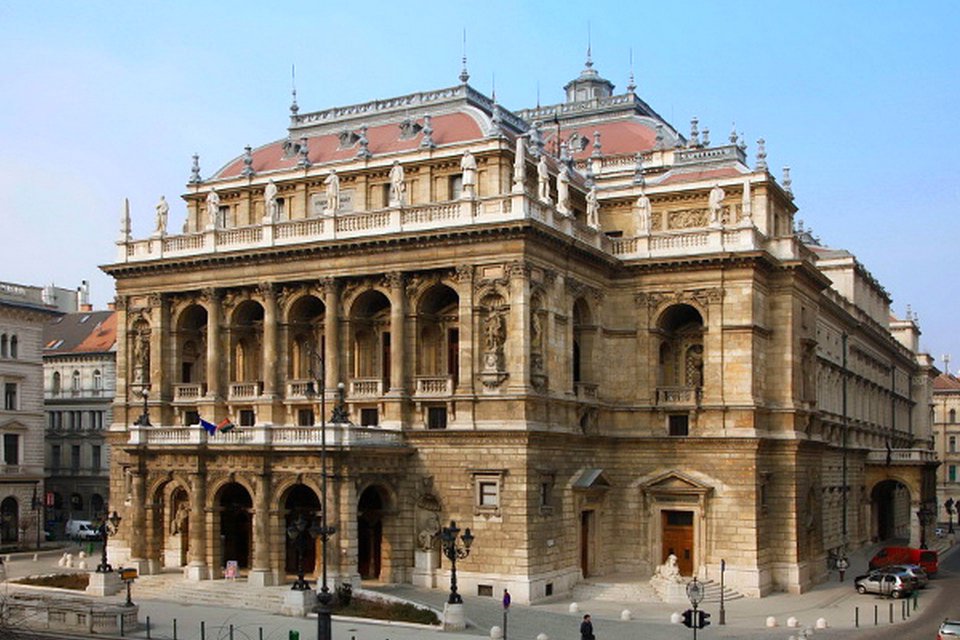
A historical building in the heart of Budapest
After a public tender, the Hungarian Opera House was built in 1873 by the renown Hungarian architect Miklós Ybl. The project started in 1875 and was completed nine years later, after smaller delays. The opening night was held on September 27, 1884, and the Emperor and King Franz Joseph were invited. Before the closure of the "Népszínház" in Budapest, it was the third largest opera building in the city. Nowadays is the second largest house both in Budapest and in Hungary.
The building restoration and its challenges
The aim of the CÉH company was to conduct an inspection, not only of the Hungarian State Opera House but also of their nearby buildings like warehouses, offices, and workshops, and develop an architectural model of the actual situation of them based on the point cloud data. To gather this information the use of Trimble RealWorks 10.0 and Faro Scene 5.5 was necessary. The process of obtaining the information was faster than process it, because of the complicated structure and spaces of the building.
The capturing and the processing process created additional difficulties too. All the scanned point cloud detail had to be accurate so it could fit into a developing model based on the previous material. There was no time available to renovate the existing materials. The scan was done while the Opera House was still in use, so it was impossible to get the complete information of the buildings and there were inaccessible rooms and warehouse too. Therefore it took many rounds until a full block could be completed, and it required significant administrative work.
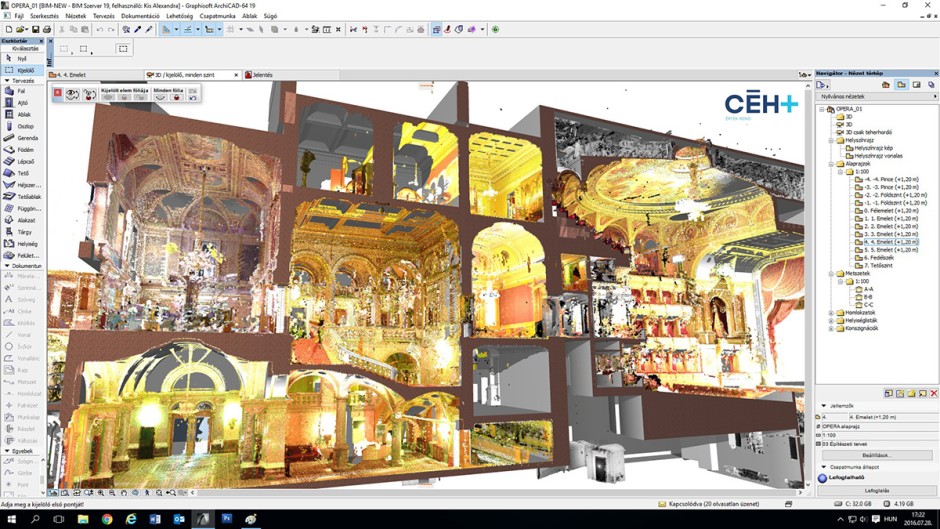
In the beginning, the multiple spheres and checkerboards were accidentally moved by the workers of the Opera which made the surveyors work more difficult. Not only elements but also certain spaces like the props warehouse were always changing and surfaces like the backstage made the process of obtaining proper measurements harder. However, with time both groups get along with each other and were able to work together.
The vaulted and sometimes zig-zag spaces of the auxiliary and mechanical of the building on the lower levels become the most difficult part of the job. Props and other equipment didn’t help to clear surfaces like walls and floors. In these cases, the results of the scan will be based in a few rough 3D models. Photos and images could be very helpful to complete the details the scanner can’t provide.
The untreated data was imported to Faro Scene 5.5 to be processed and Trimble RealWorks 10.0 to conclude the measurements. This process took time and the exported point cloud files were very large.
Cloud library
The size of the files was a problem for their management. An enormous amount of point clouds was produced, around 40 million per room, and it was unable to connect them the way they were. To reduce its size the use of Trimble RealWorks was required. This allowed to cut off the digit and connect smaller point clouds of 3-4 million points. Blocks of 20-30 million points were gathered with this reduced size with a maximum density of 1 point per sq cm. All this information was suitable to work in ARCHICAD.
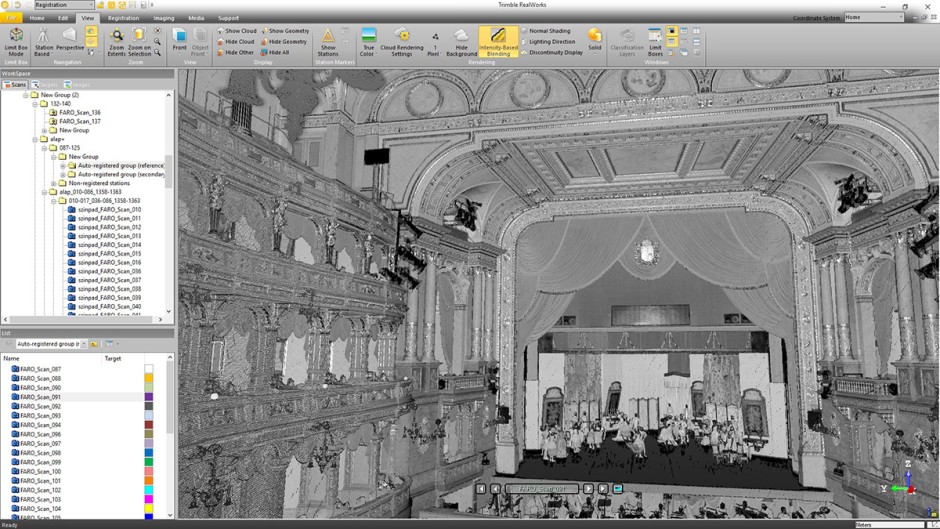
Once the reassembled point cloud file was exported in E57 format, comprehensible for the design software, the architectural team begin their work. For the modeling process, the team used ARCHICAD 19 and for the files management GRAPHISOFT BIMcloud, because it provided a global access to any file. The size of the full project exceeded the 50 Gb.
Developing a model
In this case, the biggest restraint for the architects was the hardware capacity because of the size of both the point cloud and the file model. This made the management of the project more complicated, but it was solved by using a few tricks that reduced the size of the project. Getting rid of components like library elements and save redundant elements as Objects in order to make the 2D navigation smoother. Then, any object could be placed as many times as necessary as an alternative to multiple Morphs or other elements.
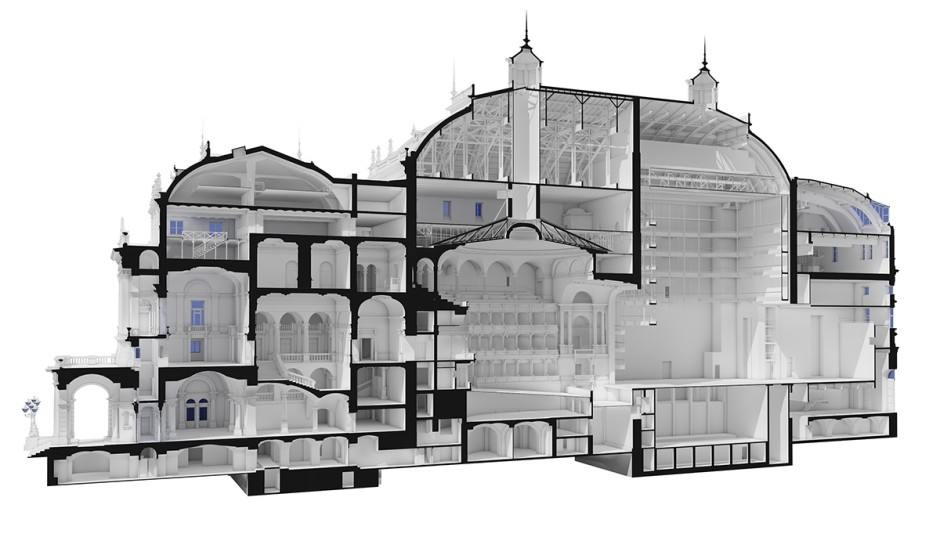
With the combination of smart layers, 3D navigation and additional 3D modeling became more handleable. The final result was a building model open for anyone to explore, and it required all the survey to be planned and scheduled in detail because the team couldn’t access all the parts of the building.
The continuous and effective work and effective work of the surveying and modeling tasks required the constant cooperation between the staff of the Hungarian State Opera House and the CÉH team of engineers.
Type of Work
- Building