Technical Area | Articles
The place to solve all your BIM doubts
3D Laser Scanning in BIM
Lean & Industrialized construction Project IPD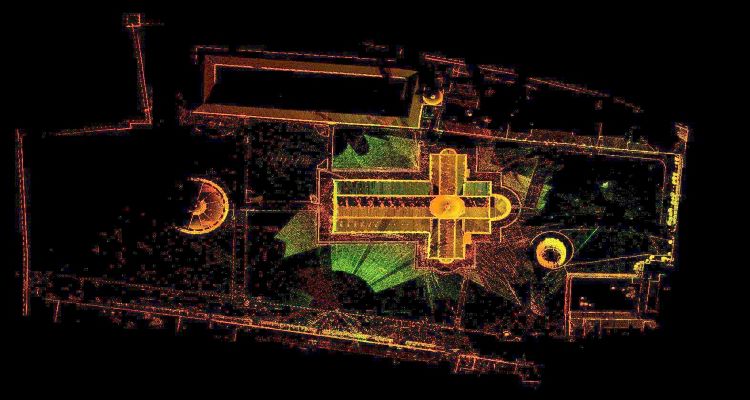
So…What is 3D Laser Scanning?
3D Laser scanning implies the use of lasers to capture 3D spatial data in the form of a point cloud data consisting of 3D coordinates. It is a popular technique of collecting data from surfaces of a physical space or site, objects, buildings etc. with accurate measurement and high speed.
How does the 3D scanner work?
The 3D scanners use lasers that takes multiple snapshots of an object or site from the placed location. The shots are then fused into a 3D model, an exact three-dimensional copy of the object, which you can rotate and view from different angles on your computer. The laser scanning system once placed, by throwing out light waves it travels certain distance, hits the solid surface/object and then returns back to the sensor. The sensor calculates the distance travelled by the light beam, which is processed and this data is termed as point cloud data which is then populated by millions of measurements, thus, forming a digital and virtual representation of the scanned objects and surfaces.
The scanning process can be performed in the following ways:
- Time-of-Flight Scans: This involves measuring the distance between the horizontal and vertical angles for every position. Hence, the scanner head occupies all the grid positions for every scan.
- Phase-based Scans: The scanner measures the phase shift of the returning laser energy to calculate distances.
- 360 degree scans: Entire 360 degree measurement.
- Triangulation: This method is used for short range scans (0.5-2m) collecting data to micron level accuracy. It is usually used to scan the detailed features of an object.
Some of the 3D Laser Scanner providing companies are:
- Topcon etc.
What are the steps of the Scanning process?
- Identification of information required for project
- Planning for the Scanning to be executed
- Scanning the site/building
- Collection of Data
- Using it in BIM process for 3D Modelling
Some of the formats in which the scanned data is collected:
- .fls
- .las
- .rds
- .ptg
- .ptx
- .pcg
- .zfs
- .xyz etc.
How do BIM and Scan to BIM correlate?
Building Information Modeling is the process of creating digital representations of functional and physical characteristics of spaces/facilities. BIM is important to the AEC industry as it allows businesses to approach projects with a higher level of insight and predictability.
Is 3D Laser scanning only meant for conservation og historical monuments and renovations?
The answer is certainly no…3D Laser Scanning can also be used for new construction projects. It assists the engineers to survey the site, make a model and incorporate the necessary changes if required before the development phase initiates. In case of existing projects it can be used to create a record of the environment and adjacent buildings and structures before demolition. Thus, Laser scanning can be deployed in a new construction project to facilitate the BIM process.
What are the benefits of 3D Laser Scanning?
- Quick and qualitative collection of Data: It is the quickest method as laser scanners can collect millions of data points in seconds, reducing the delay and human resources needed to carry out surveys.
- Maximizes efficiency: It reduces a large degree of human error by eliminating human involvement in scanning and thus, maximizes efficiency.
- Reduces Health and Safety Hazards along with surveying inaccessible areas: Surveyors can stay safe by using laser scanners to collect information from dangerous or hard-to-reach locations without putting themselves at risk. Laser scanners also aid in collecting point cloud data from inaccessible areas which were once off-limits.
- Detailed 3D Models Can Be Created from Scan Data: The biggest advantage of laser scanning is that the scanned data can create 3D BIM models on which further analysis, simulation, walk-throughs etc. could be done.
- Accelerates decision making: It facilitates faster decision-making and project alterations there is improved transparency, collaboration and effective communication amongst stakeholders and team members.
- Reduces unnecessary costs and rework: Reduction in rework can reduce the construction cost, as well as help in maintaining timeline of the projects. By knowing which materials are needed and determining their actual costs could help in significant savings.
Thus, 3D Laser scanning can add great value to the BIM process. This is proving to find popularity in the AEC industry. Moreover, the extensive use of point cloud technology by AEC professionals is helping them to optimize the BIM process and achieve great results. That’s why, application of 3D laser scanning to BIM is sensible.
-BIM will make it easy!!